Three faults of three-phase motor stator windings and two connection methods
2021-05-23
What is a three-phase motor
Three-phase motor means that when the motor's three-phase stator winding (the phase difference of 120 electrical degrees), after the introduction of three-phase AC, will generate a rotating magnetic field, the rotating magnetic field cuts the rotor winding, resulting in induced current in the rotor winding ( The rotor winding is a closed path. The current-carrying rotor conductor will generate electromagnetic force under the action of the rotating magnetic field of the stator, thus forming electromagnetic torque on the rotating shaft of the motor to drive the rotation of the motor, and the direction of rotation of the motor is the same as that of the rotating magnetic field.
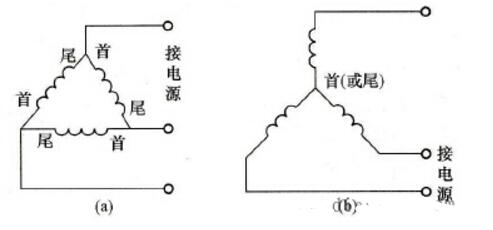
Three-phase asynchronous motor stator winding two connection methodsA three-phase asynchronous motor has three-phase windings, which are separated by 120° space and are respectively embedded in the stator iron core, that is, two or two heads or two tails are spaced 120° apart. Each phase winding has two outgoing ends, ie, one tail and one tail. The stator winding connection method mainly includes two kinds of triangle connection and star connection.
(1) Triangle connection. That is, three-phase windings are connected end to end to form a closed loop. As shown in Figure (a), three lines are drawn at the connection point at the end and the end, respectively, to connect the three-phase power supply.
Two kinds of connection methods of stator windings of three-phase asynchronous motor
(a) triangular connections; (b) star connections
(2) Star connection. It is to connect the three heads or three tails of three-phase windings together to form a star point, and the Other three tails or three heads are connected to the power supply, as shown in (b).
According to regulations, the head and tail of the six lead lines are U1, V1, W1, U2, V2, and W2, respectively (the heads and tails of the old labels are D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, and D6, respectively). among them:
U1, U2- Head and tail of the first phase winding.
V1, V2 - The head and tail of the second phase winding.
W1, W2 - Head and tail of the third phase winding.
Four-phase asynchronous motor winding fault analysis and processing Fault one: winding groundingRefers to grounding caused by damage to the windings and the insulation or the insulation of the enclosure.
1, the phenomenon of failure
Enclosure electrification, control circuit out of control, winding short-circuit heat, resulting in the motor can not operate normally.
2, the reason
Insulation resistance decreases due to moisture in the windings; Long-term overload operation of the motor; Corrosion of harmful gases; Ingress of metal foreign materials into the windings to damage the insulation; Insulation damage to the stator winding when rewinding the iron cores; End caps of the windings touch the base; Insulation burns due to stator and rotor friction Leading line insulation damage collided with the shell; overvoltage (such as lightning) makes insulation breakdown.
3. Inspection method
(1) Observation method. Visually inspect the insulation at the ends of the windings and in the raceway for signs of damage and charring, and if so, the grounding point.
(2) Multimeter inspection method. Use a multimeter to check the low impedance file. If the reading is small, it is grounded.
(3) Megaohmmeter method. According to different levels, different megohmmeters are used to measure the insulation resistance of each group of resistors. If the reading is zero, the windings are grounded, but it is necessary to determine the insulation of the motor due to moisture or breakdown due to accidents. Generally speaking, The pointer oscillates arbitrarily at "0" and it is assumed that it has a certain resistance value.
(4) Test light method. If the test light is on, it means that the winding is grounded. If a spark or smoke is found somewhere, this is the winding ground fault point. If the lamp is slightly bright, the insulation has a grounding breakdown. If the lamp does not light, but the test rod is also grounded when the spark, indicating that the winding has not yet penetrated, but severely damp. Hardwood can also be tapped on the edge of the shell's mouth, knocked to a place such as a light off, indicating that when the current off, then there is the ground point.
(5) Electric current burning method. With a voltage regulator transformer, after the power supply is connected, the grounding point will quickly heat up, and the insulation smoke will be the grounding point. Special attention should be paid to the fact that small motors must not exceed twice the rated current and the time should not exceed half a minute; large motors should be 20%-50% of the rated current or gradually increase the current, and should be powered off immediately when the grounding point is smoked.
(6) Group elimination method. For the grounding point inside the core and the burning is severe, the burned copper wire is fused with the iron core. The method used is to divide the grounded one-phase winding into two halves, and so on, and finally find the grounding point.
In addition, there are high-pressure test method, magnetic needle exploration method, industrial frequency vibration method, etc., which will not be introduced here.
4. Treatment method
(1) The grounding of windings caused by moisture should be dried first. When it is cooled to about 60-70°C, it is poured with insulating paint and dried.
(2) When the insulation at the end of the winding is damaged, re-insert the insulation at the grounding, paint, and then dry.
(3) When the winding grounding point is in the slot, the winding should be re-wound or some of the winding components should be replaced.
Finally, use different megohmmeters to measure and meet the technical requirements.
Fault 2: Winding short circuitDue to excessive motor current, excessive power supply voltage fluctuations, single-phase operation, mechanical bumps, poor manufacturing, etc., insulation damage is caused, and the windings are short-circuited by windings, short-circuited between windings, short-circuit between windings, and short-circuit between windings.
1. Failure phenomenon
The magnetic field of ions is unevenly distributed, and the three-phase current is unbalanced, which makes the vibration and noise of the motor intensify. In severe cases, the motor cannot start, and a large short-circuit current is generated in the short-circuit coil, causing the coil to rapidly heat and burn.
2. Cause
Long-term overload of the motor causes insulation aging to lose insulation; damage caused by inserting wires; insulation breakdown caused by dampening of windings; lower insulation resistance of the windings; insulation damage at the end and interlayer insulation material; or insulation damage at the end connection wires Overvoltage or lightning strikes the insulation breakdown; rotor and stator winding ends rub against each other to cause insulation damage; metal foreign objects fall into the motor and there is too much oil.
3. Inspection method
(1) External observation method. Observe whether the junction box and the winding end are burnt. After the windings overheat, leave a dark brown color and smell.
(2) Temperature inspection method. No-load operation for 20 minutes (stop immediately when abnormality is found), touch the windings to check if the parts exceed the normal temperature.
(3) electricity test method. With ammeter measurement, if the current of a phase is too large, there is a short circuit in the phase.
(4) Bridge inspection. Measure the winding DC resistance, the general phase difference should not exceed 5% or more, if exceeds, then the resistance has a short circuit fault.
(5) Short-circuit detector method. If there is a short circuit in the measured winding, the steel plate will vibrate.
(6) Multimeter or Megohmmeter method. Measure the insulation resistance between any two phase windings. If the reading is very small or zero, it means that there is a short circuit between the two phases.
(7) Voltage drop method. After the three windings are connected in series, they are connected to low-voltage safe alternating current.
(8) Current method. When the motor runs at no load, the three-phase current is measured first, and the two-phase measurement is replaced and compared. If the change does not change with the power supply, the one-phase winding with a large current has a short circuit.
4. Short-circuit processing method
(1) The short-circuit point is at the end. Insulating materials can be used to separate the short-circuit points, and the insulated wires can also be re-packaged, and then painted and re-dried.
(2) Short circuit in the slot. After it is softened, find the short-circuit point repair, put it back into the slot, and then paint and dry it.
(3) For each phase winding with less than 1/12 of the short circuit turns, cut off all the short-circuit lines when the number of turns is connected, and connect the conducting parts to form a closed circuit to supply them for emergency use.
(4) When the number of turns in the winding short-circuit point exceeds 1/12, the rewinding must be completely removed.
Fault 3: Winding short circuitDue to poor welding or the use of corrosive fluxes, the welds may not be removed after welding. They may cause pot welding or loosening. Wires that are subject to mechanical stress or a short circuit during a collision, short circuits, and ground faults can cause the wires to burn out. When one or several wires in the wire are short-circuited, the other wires increase in temperature due to the increase of the current, causing the winding to heat and open circuit. It is generally divided into a phase winding end breakage, a turn-to-turn short circuit, a parallel branch circuit break, multiple conductors and a burnout, and a rotor break cage.
1. Failure phenomenon
The motor cannot start, the three-phase current is unbalanced, there is abnormal noise or vibration, and the temperature rise exceeds the allowable value or smoke.
2. Cause
(1) Break or create quality problems during inspection and maintenance.
(2) Wrong welding of each component of the winding, pole (phase) group, and wiring and lead wires such as the lead wire, long-term operation overheating and desoldering.
(3) The windings are damaged or broken due to mechanical and electromagnetic forces.
(4) The windings are seriously scorched or broken due to short circuit and grounding between turns.
3. Inspection method
(1) Observation method. Most of the breakpoints occur at the end of the winding, see if there is a break, and if there is a break in the joint.
(2) Multimeter method. Using a resistance file, a "Y" type connection is made by connecting one bar to the center point of the "Y" shape, and the other one is connected to the first end of the three-phase winding in turn. The infinite one phase is the break point. After the short connection of the delta connection method, each group of windings is measured separately, and the infinity is the disconnection point.
(3) Test light method. The method is the same as before, and the unlit phase is an open circuit.
(4) Megaohmmeter method. A phase whose resistance tends to infinity (that is, not a zero value) is a trip point.
(5) Ammeter method. When the motor is running, the three-phase current is measured by the current meter. If the three-phase current is unbalanced and there is no short circuit phenomenon, the one-phase winding with smaller current has some short-circuit faults.
(6) Bridge method. When the resistance of one phase of the motor is greater than that of the other two phases, it indicates that the phase winding has partial open circuit faults;
(7) Current balance method. For "Y" type connection, the three-phase windings can be connected in parallel and the low-voltage and high-current alternating current can be connected. If the current difference in the three-phase winding is greater than 10%, the small current end is open circuit; for "△" For the type of connection, one contact of the stator winding is first opened, and then a low-voltage and large-current is passed through one by one, in which a phase with a small current is an open circuit.
(8) Broken cage detector inspection method. When checking, if the rotor is broken, the millivolt reading should be reduced.
4. Open circuit processing method
(1) When the circuit is broken at the end, it shall be firmly welded after being connected, covered with insulating material, put on the insulating tube, tied and then dried.
(2) Windings New windings should normally be replaced due to severe burn-out of windings due to interturn, phase-to-phase short circuits and grounding.
(3) Emergency handling is performed for the break point in the groove, which belongs to a small number of break points. A breakout point method is used to find the break point, and it is used after the winding is disconnected and the insulation is qualified.
(4) The caged cages can be repaired by welding, cold-bonding or strip change.
Fault 4: Wrong windingWinding connection error causes incomplete rotating magnetic field, causing difficulty in starting, unbalanced three-phase current, large noise and other symptoms. If it is not treated in time, it will burn out the winding. There are mainly the following situations: One or more coils in a certain polar phase are embedded or connected head to tail; the polar (phase) group is reversed; the winding of one phase is reversed; the parallel winding branch of multiple paths is connected incorrectly; "Y" wrong connection.
1, the phenomenon of failure
The motor cannot start, the no-load current is too large or the imbalance is too large, the temperature rises too fast or there is severe vibration and there is a lot of noise, and the fuse is blown.
2, the reason
Misconnect the "△" type into "Y" type; one phase of the three phase winding is reversed during maintenance; the decompression start is inappropriate selection of tap position or internal wiring error; the winding connection is wrong when the new motor is offline; The motor failed to judge correctly.
3 maintenance methods
(1) Ball method. If the ball rotates and rolls along the inner circumferential surface of the stator, it means that it is correct, otherwise the winding may be miswired.
(2) Compass method. If the windings are not connected incorrectly, then in one phase winding, when the compass passes through the adjacent pole (phase) group, the polarity of the fingers should be reversed, and the polar (phase) groups of adjacent phases in the three-phase windings are also On the contrary, if the polarity direction is constant, it indicates that there is a pole (phase) group reverse connection; if it is indefinite, there is a reversed coil in the phase group.
(3) Multimeter voltage method. According to the wiring diagram, if there is no indication on the two measured voltmeters, or if there is one reading and one reading at a time, it indicates that the windings are connected reversely.
(4) Common methods include dry battery method, milliammeter remanence method, and motor steering method.
4. Treatment method
(1) If a coil or coil group is connected reversely, the no-load current has a large imbalance and should be returned to the factory for repair.
(2) Leading line errors should be correctly judged before and after reconnection.
(3) The decompression start error should be checked against the wiring diagram or schematic diagram, and carefully re-wiring.
(4) After the new motor is disconnected or reconnected to the new winding and the wiring is wrong, it shall be sent to the factory for repair.
(5) When the stator windings are connected in opposite phase, the reversed phase current is particularly large. Faults can be found and repaired according to this characteristic.
(6) When the "Y" type is connected to "△" type or the number of turns is not enough, the no-load current is large and should be corrected in time.
Three-phase asynchronous motor stator winding fault repair 1, fault winding fault repairPractical experience shows that the majority of open circuit faults occur near the ends of the motor windings, the terminals of the winding elements, or the leading end of the motor. Since the ends of the windings are exposed outside the motor core, the wires are easily broken or the terminals are loose due to welding, and they will loosen during long-term use. Therefore, the ends of the windings must be inspected first. If disconnected wires or joints are loosened, , should be re-welded, coated with insulation and then coated with insulating paint can be used. In addition, windings are blown due to faults such as short-circuits between the windings and the ground. Most of the windings need to be replaced.
When the small motor is checked for an open circuit, it can be verified with a megohmmeter or a multimeter and a check lamp. For a star-connected motor, each phase must be tested separately during inspection, as shown in Figure 1. For delta-connected motors, the three-phase winding terminals must be dismantled for inspection and tested separately for each phase, as shown in Figure 2.
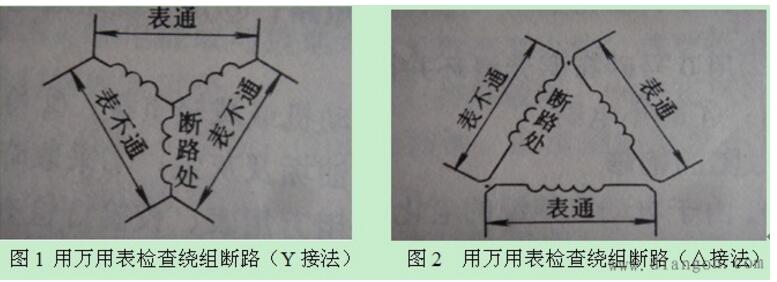
Most of the medium-capacity motor windings use a plurality of wires and are connected in parallel with a plurality of branches. Among them, if several roots are disconnected or one is disconnected, the inspection is complicated. Usually the following two methods are used.
(1) Three-phase current balancing method For the three-phase windings of the star-connected motor, the three-phase windings are connected in parallel, and low-voltage and high-current are passed. If the three-phase current is more than 5%, one phase with small current is the open phase.
(2) The resistance method uses the bridge to measure the resistance of the three-phase windings. If the difference in the three-phase resistance value is greater than 5%, the one with the larger resistance is the open phase.
2、Overhaul of winding faultsMotor windings commonly known as "collision." Damage to the motor windings, insulation ageing, and damage to the slot insulation or over-insulation of the insulation during overhaul of the windings can cause ground faults.
Inspection method: Use the low block of the multimeter and the check lamp below 40W to check phase by phase according to Figure 3.
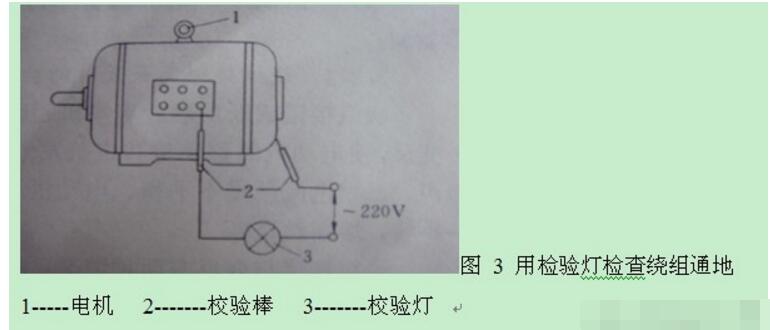
If the resistance is small or the check lamp is dark red, it means that the phase winding is heavily damp and should be dried. After drying, it can be used when it is measured with a megohmmeter and its insulation resistance is greater than 0.5 megohms. If the resistance is zero or the check lamp lights up, it is the ground phase. Then check the insulation of the earth-phase windings. If cracks and scorch marks are present, it is the pass-through point. If it is difficult to see the scorch marks, measure the phase winding with a megohmmeter. If you smoke, you can find out where.
3, maintenance of winding short circuit faultWinding short circuits are generally caused by overvoltage, undervoltage, overload, or two-phase operation. Check the fault should first understand whether the motor overload, overvoltage or two-phase operation and other abnormal conditions, short circuit due to the current is too high and produce high heat, so that the insulation is crisp, observe the motor windings have burnt marks and burnt smell.
Winding short-circuit conditions include short-circuit between windings, short-circuit between windings and windings, short-circuit between polar groups, and short-circuit between phases. Commonly used inspection methods are as follows:
(1) Use Megohmmeter or multimeter to check the phase insulation Use a megohmmeter or multimeter to check the insulation resistance between any two phases of windings. If the insulation resistance is very low, it means that the two phases are short circuited.
(2) Current balance method
(3) The resistance method uses a bridge to measure the three-phase winding resistance. A phase with a small resistance is a short-circuit phase.
At present, there are mainly three starting methods for a 9000 kg/h yarn making motor: direct start, soft starter control start, and inverter control start. Among them, the motor with small power usually adopts the direct start method. In the production, it needs to use the frequency converter to control the start and speed control, and for the high-power fan, it uses the soft starter to start. In combination with the actual production situation, for sudden equipment failure caused by the motor in the production process, in order to not affect the production and product quality, the most efficient way is usually adopted, that is, to quickly determine the occurrence of a fault (soft or hard). Excluded immediately, can be replaced by replacement, and can't be replaced immediately. (http://copyright.com) Soft faults are the faults that are usually caused by the program (very many occur, the system runs for a long time is relatively stable), and the other ones are the hard faults, that is, the faults caused by the components. The incidence of this part of the fault is relatively high, the search from the control (auxiliary contacts) and the main circuit in two parts, usually the main circuit in a certain order: power supply - feeder (including air switch and contactor parts) - - Disconnector - motor.
The following are two small cases encountered in the production and maintenance process. Failure of FB2 Belt Conveyor Motor and MB36# Raw Stem Silk Storage Cabinet Screw Motor.
Symptom: The air switch trips, the motor heat can not run "? Xml: namespace prefix = v ns = "urn:schemas-microsoft-com:vml" /"
Fault check and troubleshooting: Check the power supply is no problem, the feeder is also good, but check the three-phase resistance unbalance of the motor from the outlet end of the feeder. The motor terminal box is opened and the outlet of one of the windings is blown. Reconnect processing, starter motor is running well.
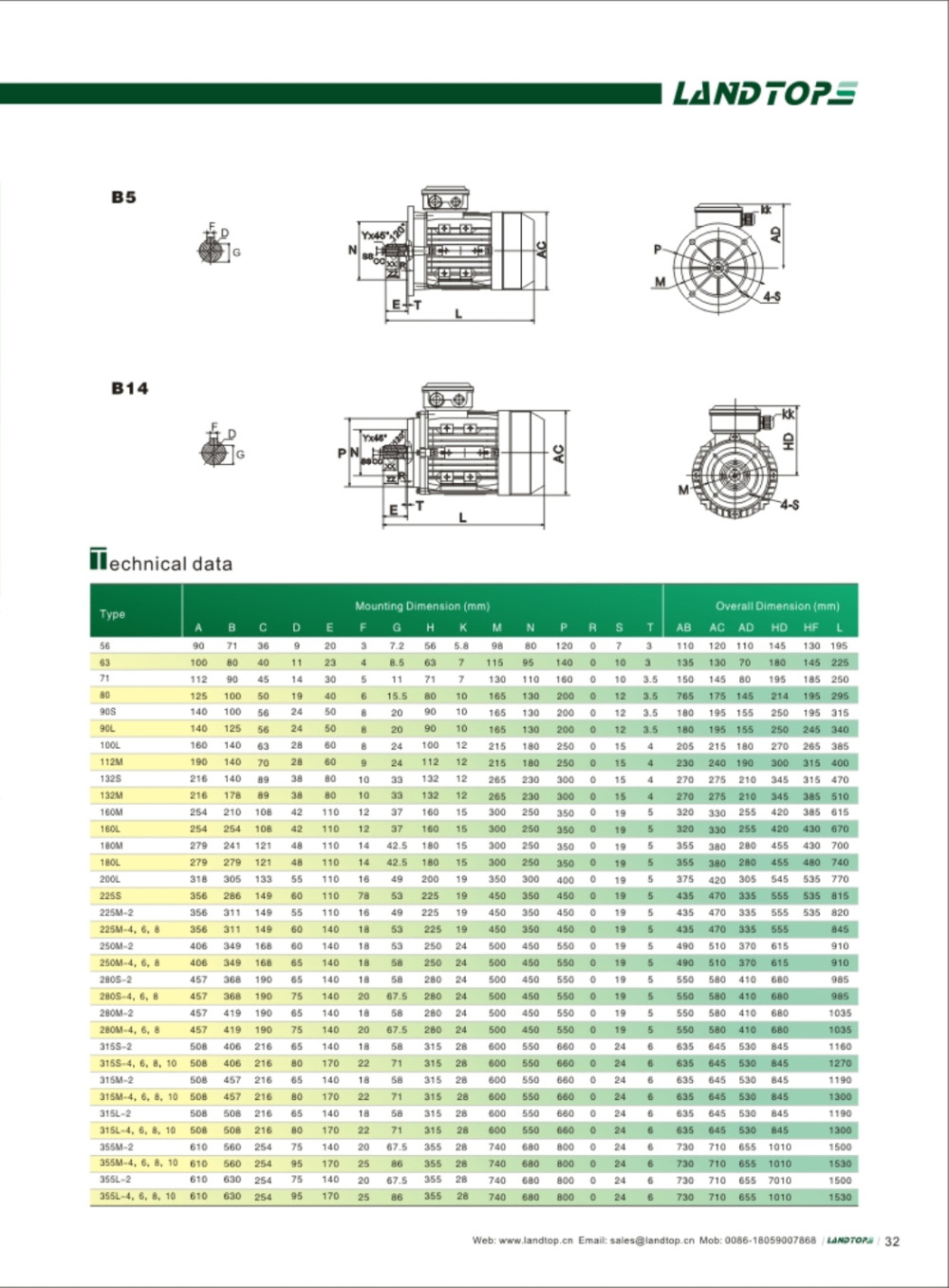
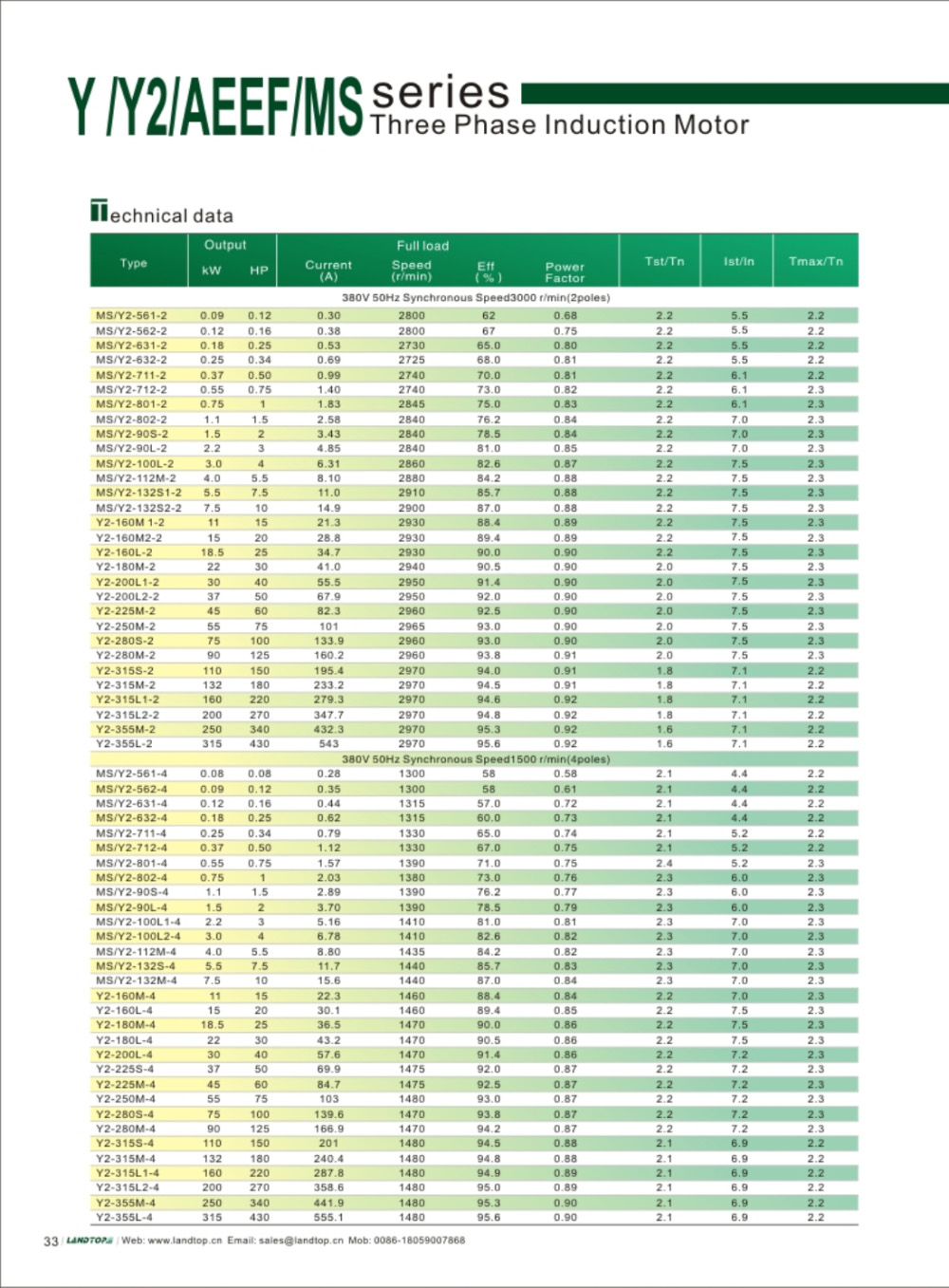
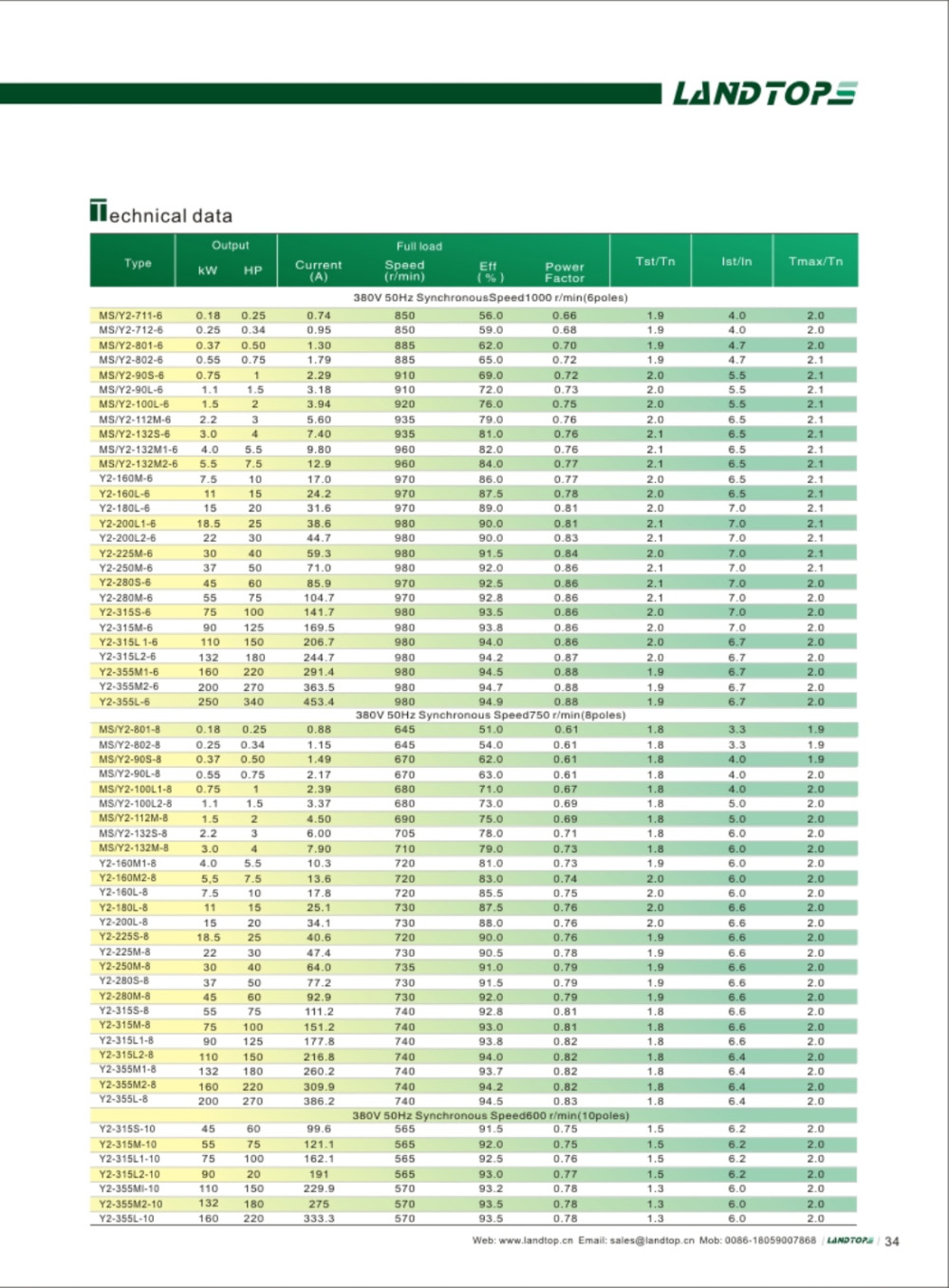
Y series 3-phase cast iron housing induction motor
Y series motor is totally enclosed and fan cooled three phase squirrel cage induction motor. It is newly designed in conformity with the relevant rules of IEC&DIN42673 standards. The Y connection for motor of 3kw and below. And delta connection for 4kw and above.
Application:
Y series motors are widely used in places where there doesn't exist combustible, explosive or corrosive gas, and without any special requirements, such as machine tools, pumps, fans, transport machinery, mixer, agriculture machinery and food machines, etc.

3 Phase Motor, Three Phase Motor, 3 Phase Induction Motor, Three Phase Electric Motor
HENGTAI INTERNATIONAL CO., LTD. http://www.landtopcos.com








